What is it?
Cymatherapy sessions deliver sound wave frequencies through the body using the Chinese medicine meridian pathways on the feet and hands. These sessions deliver the “sound nutrition” of 5 frequencies and tones combined together in specific combinations to address different disharmonies and imbalances in the body.
How does it work?
Sit comfortably for 30 minutes while you rest your feet or hands directly on our cymatherapy device. One of twenty specific health frequency protochols will be chosen to run for you, dependent upon your health needs and goals.
Cymatherapy’s history
Dr. Manners at 101 years old. He attributed his long life and good health to the power of the vibrational codes he discovered and applied on a daily basis at his clinic.
Cymatherapy is based on the work of Dr. Peter Guy Manners, a British Osteopath who started in the 1940’s. Dr. Manners dedicated his life’s research to sound therapy and its application to healing. After decades of research, he developed around 750 vibrational codes for precise physiological and energetic functions; frequencies that were identified to restore tissues, organs, glands, bones etc. (as well as for more subtle phenomena) to their natural healthy resonance.
Combining 5 frequencies together was a major key to unlocking the potential of Cymatherapy; full results were not found when using 1, 2, 3, or 4 sound frequencies together. Dr. Manners also found that the audible sound alone was not sufficient for optimal healing. It did not have a great enough effect. Instead, a coherent acoustic wave driven by a transducer directly into body tissue was needed.
Physical Injuries Research
Cymatherapy was adopted for Veterinary use when it first came to the United States. It was found to be great value in injuries to horses, for example tendon tears in racehorses (similar to tears to the achilles tendon in human athletes.) It is common for racehorses to be put down (killed) if they suffer tendon tears which are deemed too major to recover from.
The image to the right shows ultrasound proof of the amazing healing of a 95% tendon tear in a racehorse, which was thought to be irreparable. Not only did this massive tear heal in only six weeks, it did so with no scarring or adhesions, which is a revolutionary level of success with such a severe injury.
Many human athletes have also found the tremendous benefits of Cymatherapy. The virtual disappearance of inflammation in a chronic leg injury of a Triathlete after only 20 minutes of Cymatherapy, with the absence of inflammation still held a full day later in a Thermography scan.
Inflammation Research
Inflammation plays a role in a wide range of degenerative illnesses and has been associated with many serious health issues, including: auto-immune disease, cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease/ memory loss, Metabolic Syndrome, Cancer, accelerated aging and organ failure.
Thermography is a key method for identifying inflammation with modern medical imaging. Thermography creates color images of heat levels in the body, which shows the severity of inflammation processes — and can also indicate the level of reduction of inflammation after using a particular therapy. Inflammation appears as a red color on the Thermography scans, while cooler tissue shows colors towards the blue side of the spectrum.
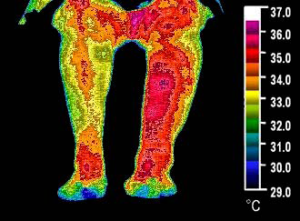
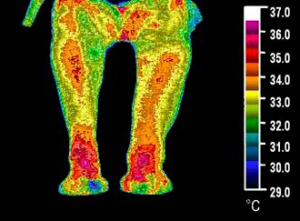
A major research project focused on Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), (a condition of the blood vessels that leads to narrowing and hardening of the arteries) was published and presented at BioElectromagnetics Society (BEMS) 30th Annual Meeting in June 2008.
As seen in the pictures below, thermography reveals a stunning decrease in inflammation after only 15 minutes of application. The “Before” pictures are on the left, the “After” pictures are on the right of the image below.
This type of anti-inflammatory result has been found in research on other parts of the body as well. It has been shown to reduce inflammation throughout the upper body, including oral cavity, breast and lymph tissue, with the sound vibrations applied through the feet after a 6 week protocol of twice weekly treatment.
Oral inflammation- bright white spots on the left image at the crowns diminish in the right picture after a 30min. session
Other research projects are ongoing, including recent projects with Alzheimer’s and with major Lung issues (COPD, emphysema).